Global packaging waste is expected to surpass 1.3 billion tons annually by 2030, placing unprecedented pressure on governments, industries, and brands to decarbonize and redesign their material footprint.
Nestlé CEO Mark Schneider said, “Plastic waste is one of the biggest sustainability issues the world is facing today. Tackling it requires a collective approach. We are committed to finding improved solutions to reduce, reuse, and recycle. Our ambition is to achieve 100% recyclable or reusable packaging by 2025.”
But beyond public commitments, what’s Nestlé’s actual R&D strategy in sustainable packaging materials? Nestlé is rethinking its packaging system with a systematic, science-driven R&D approach for eliminating plastic waste, cutting carbon emissions, and redesigning materials for recyclability, compostability, and reuse.
Between 2021 and 2024, Nestlé has made over 200 distinct packaging innovations, many of which challenge industry norms in polymer science, biodegradable materials, and multi-barrier laminates. These innovations reflect a deep commitment to sustainability and reveal a calculated strategy to align packaging with net-zero ambitions and appeal to eco-conscious markets where 43% of consumers now cite the environmental impact of packaging as a core purchase driver.
Nestlé’s approach offers both a benchmark and a warning to brands that lag behind is that they are risking reputational costs and commercial setbacks. This article dissects Nestlé’s most recent research advancements in sustainable packaging, unveiling strategic implications for rival firms in food, beverage, and consumer goods.
Latest Research and Innovations in Sustainable Packaging Materials by Nestlé
Nestle’s strategy in sustainable packaging materials focuses on developing innovative, eco-friendly solutions to reduce environmental impact. The research explores various innovative materials and strategies to replace traditional plastics, emphasizing renewable, biodegradable, and recyclable options.
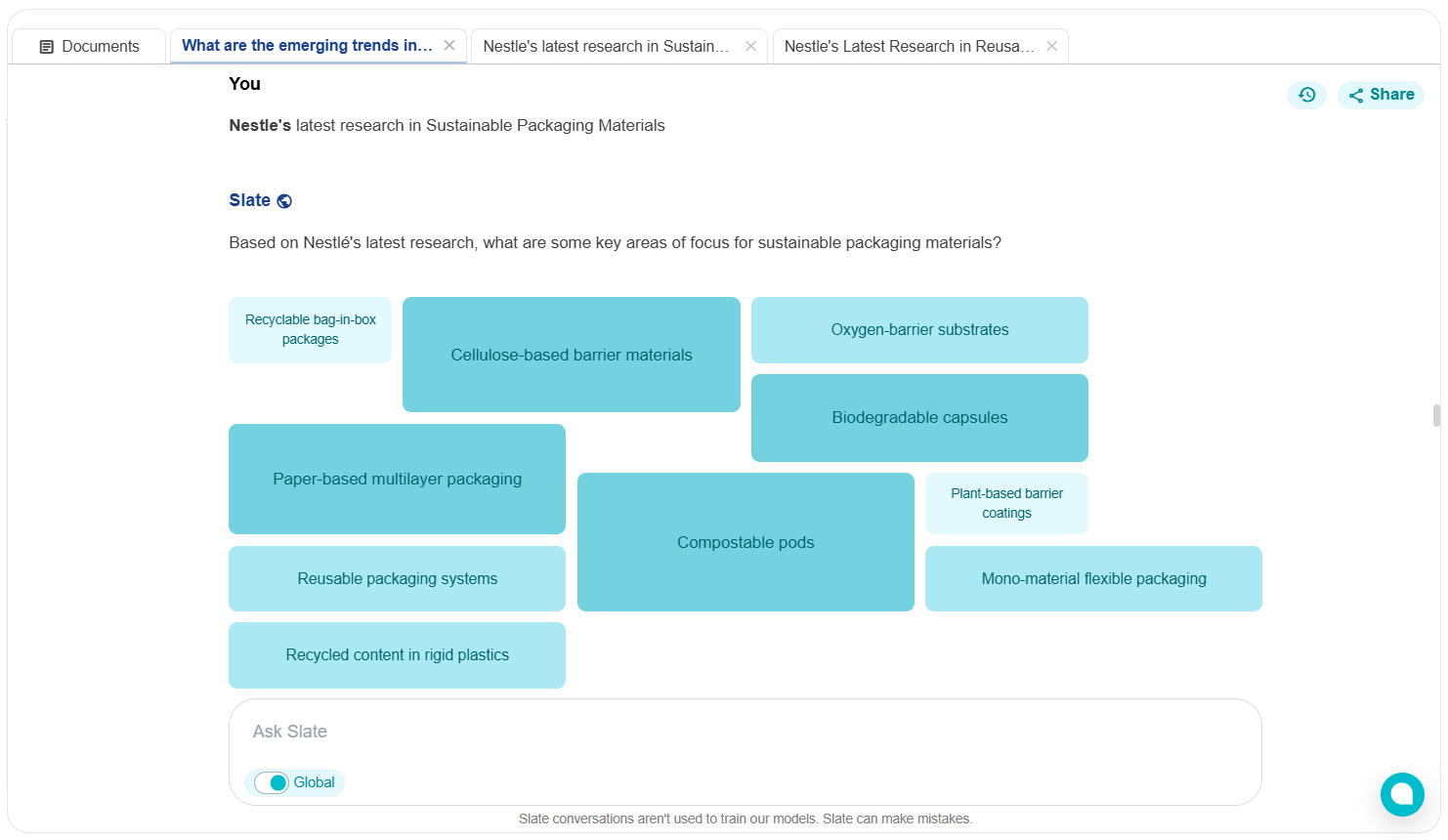
As R&D heads and innovation managers aiming to track such rapid advancements, navigating scattered research papers, patents, and sustainability reports can be overwhelming. This is where AI-powered tools like Slate can help consolidate Nestlé’s latest packaging research and innovations into structured, actionable insights.
Slate synthesizes complex data into key themes, providing a holistic view of Nestlé’s sustainable packaging roadmap. It also allows researchers to do side-by-side comparison of all the technical solutions to objectively evaluate their strengths, weaknesses, and suitability for addressing specific research problems.
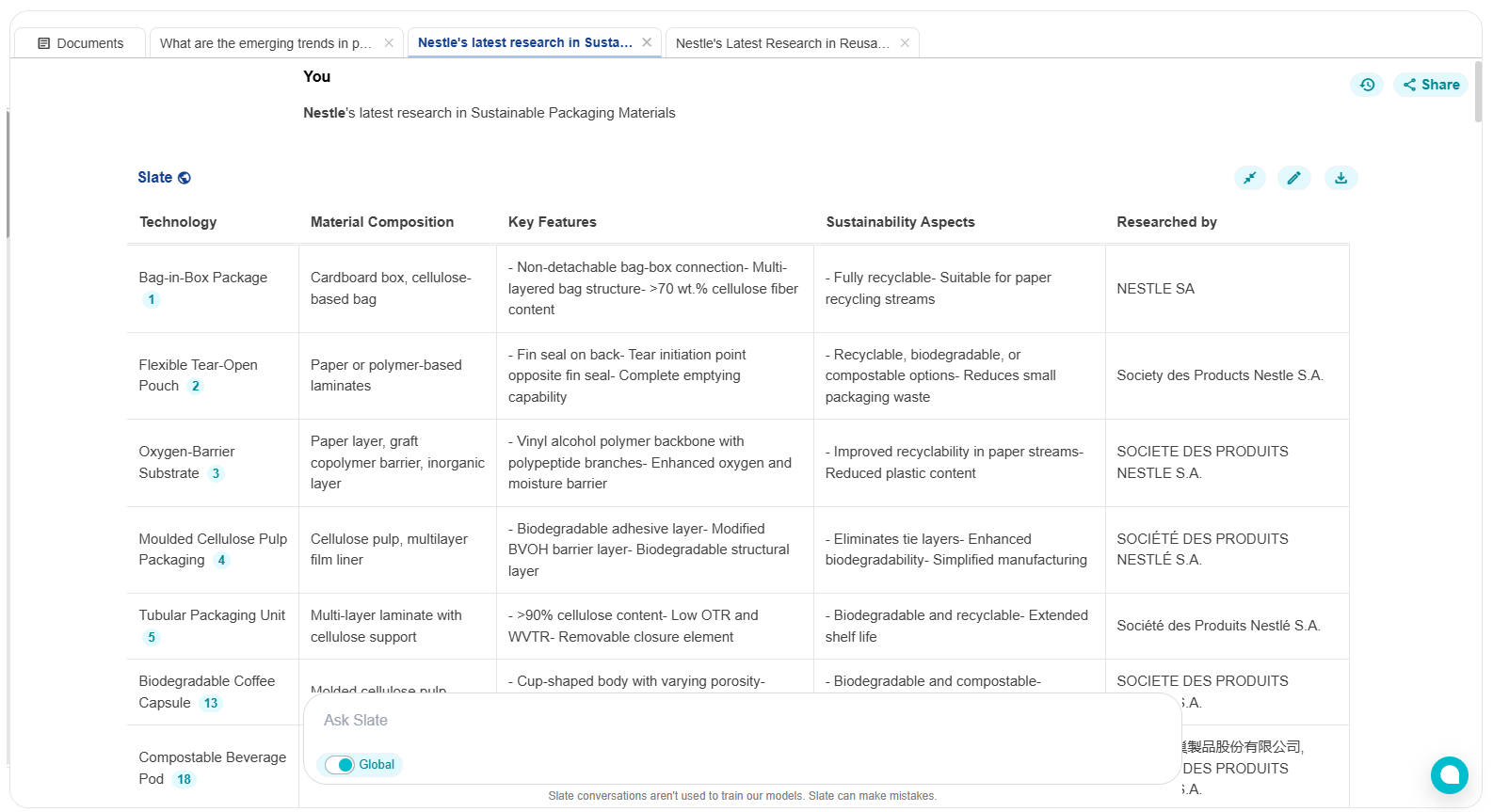
This enables companies to monitor where Nestlé is investing, benchmark progress, and adjust their R&D strategies accordingly. For organizations competing in food & beverage, or consumer goods, such real-time intelligence offers an invaluable early-warning system.
Let’s explore the key themes and features identified from the research:
1. Recyclable and Biodegradable Packaging Solutions
Nestlé is developing designs that ensure packaging components can be recycled together without contamination, addressing one of the core challenges in the circular economy.
Bag-in-Box Packaging: This design uses recyclable materials suitable for paper recycling streams. It features a cellulose fiber box and a cellulose-based bag with barrier functions. The integration ensures both components are recycled together, minimizing environmental impact.
Flexible Tear-Open Pouch: Designed to remain intact after opening, this pouch addresses small packaging waste issues. It can be made from recyclable, biodegradable, or compostable materials, enhancing recyclability and providing a cost-effective solution for single-use applications.
2. Advanced Barrier Materials for Shelf Life Extension
Preserving shelf life without relying on complex plastics is central to Nestlé’s materials science research.
Oxygen-Barrier Substrate: This substrate incorporates a graft copolymer with a vinyl alcohol polymer backbone and polypeptide branches, enhancing its barrier properties against oxygen and moisture. This structure improves recyclability and reduces plastic content while maintaining excellent barrier properties.
Multilayer Film Liners: Used in rigid or semi-rigid molded cellulose pulp packaging, these liners enhance biodegradability and barrier properties, making them suitable for beverage capsules and other packaging items.
3. High Cellulose Content Packaging
Nestlé’s cellulose-based solutions offer a viable alternative to plastic across varied food applications.
Tubular Packaging Units: These units feature a multi-layer laminate with high cellulose content, achieving excellent barrier properties and recyclability. They are designed to enhance product preservation and extend shelf life.
Cylindrical Containers: Made from multi-layer oxygen and moisture barrier laminates, these containers offer high recyclability and maintain product freshness. They are suitable for food items like powders.
4. Compostable Beverage Pods
Nestlé has introduced fully compostable beverage solutions that meet consumer demand for sustainability in convenience products.
Biodegradable Pods: These pods are designed for beverage production machines. They feature a multi-layered structure with compostable materials. They maintain barrier properties while being fully home-compostable, addressing sustainability concerns with traditional pods.
Cellulose-Based Capsules: Made from molded pulp, these capsules offer a sustainable alternative to plastic or aluminum. They feature a biodegradable closing membrane and effective sealing during brewing.
5. Renewable and Biodegradable Materials
Nestlé’s exploration of renewable feedstocks signals a strategic move to decouple from fossil-derived polymers.
Bio-based Polymers: Nestle is exploring biopolymers derived from renewable sources such as plant starches, cellulose, and agricultural waste. These materials are biodegradable and compostable, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastics.
Biodegradable Polymers: The research highlights the use of biodegradable polymers like starch, cellulose, polylactic acid (PLA), and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) to create bio-based films and materials, reducing reliance on petroleum-based products.
6. Compostable and Recyclable Packaging
Targeting zero-GHG packaging systems, Nestlé is pioneering materials derived from agro-waste.
Compostable Packaging: Nestle is developing packaging solutions derived from food biowastes and agricultural residues, aiming to replace conventional plastics with compostable options that emit zero greenhouse gases.
Recyclable Packaging: The focus is on creating recyclable packaging with strong barrier properties to address ecological concerns while maintaining product stability and quality.
7. Multilayer Laminate Packaging
The company’s cellulose-dominant laminates offer dual benefits of functional integrity and sustainable end-of-life outcomes.
High Cellulose Content: Nestle’s packaging solutions often feature a high cellulose content, exceeding 90%, which ensures recyclability and aligns with sustainability goals. These materials, such as tubular and cylindrical containers, are used in various forms to provide effective barriers against oxygen and moisture.
Barrier Properties: The packaging designs achieve low Oxygen Transmission Rates (OTR) and Water Vapor Transmission Rates (WVTR), which are crucial for extending the shelf life of food products. This is achieved through the use of organic or inorganic barrier layers in combination with cellulose-based materials.
8. Advanced Coating Techniques
Nestlé is developing proprietary coatings that boost packaging resilience while retaining recyclability.
Ceramic and Composite Coatings: Nestle employs advanced coating techniques to enhance the barrier properties of molded pulp articles. These coatings, made from materials like aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, improve moisture and oxygen resistance while maintaining recyclability.
Polymer and Metal Particle Coatings: Composite phases containing polymers and metal particles applied to pulp articles create continuous barriers that enhance the packaging’s protective capabilities.
9. Innovative Design Features
Design functionality is being embedded into sustainable packaging to maximize usability and appeal.
Functional Closures: Packaging designs incorporate innovative closure mechanisms, such as the “lift & push” system, which enhances usability and product protection. These closures are designed to be ergonomic and customizable.
Fragrance Vents and Stackability: Some packaging solutions include features like fragrance vents to enhance product appeal and stackable designs for efficient storage and handling
Decode Nestlé’s Next Move in Eco-Friendly Packaging
Nestlé’s aggressive push into sustainable packaging is a coordinated, multi-year R&D strategy that blends material science, regulatory foresight, and consumer insight into a competitive differentiator. From cellulose-based laminates and compostable beverage pods to advanced barrier coatings and reusable systems, Nestlé is actively redesigning packaging to comply with future standards and shape it.
With over 200 innovations launched since 2021, Nestlé focuses on making its packaging eco-friendly and standing out from its competitors. Companies that delay investment in eco-friendly and circular packaging systems risk falling behind on customer adoption.
To stay competitive and informed on Nestlé’s ongoing R&D initiatives and packaging breakthroughs, leveraging tools like Slate is critical.
With Slate – an external innovation discovery platform
- Access consolidate Nestlé’s latest packaging R&D and innovations from diverse sources (patents, research reports, and scientific literature) into one actionable view
- Explore new packaging solutions with detailed performance and environmental impact data
- Monitor competitors’ latest material innovations, packaging strategies, and technology trends to inform your R&D roadmap
- Get data-backed answers to your packaging innovation questions via Slate’s AI research assistant


