As sustainability pressures reshape the food and beverage industry, packaging has become a key area of R&D-driven differentiation. Nestlé is advancing this front with a fully recyclable bag-in-box system made from advanced cellulose fibers, a notable shift from the mixed-material formats still common among competitors like Unilever and PepsiCo.
This mono-material approach improves recyclability without sacrificing product protection and reflects Nestlé’s broader push to make all packaging recyclable or reusable by 2025. For R&D leaders tracking innovation strategy, Nestlé’s move signals a scalable, regulation-aligned packaging solution that could influence future industry benchmarks.
This article will explore Nestlé’s latest developments in recyclable bag-in-box technology in detail, examining its material composition, scalability potential, and operational implications.
Latest Research and Innovations in Bag-in-Box Packages by Nestlé
Nestlé continues to push forward its sustainable packaging goals with the development of a fully recyclable bag-in-box package. This innovation demonstrates the company’s commitment to using eco-friendly materials while enhancing recyclability, a key focus area in their broader packaging strategy.
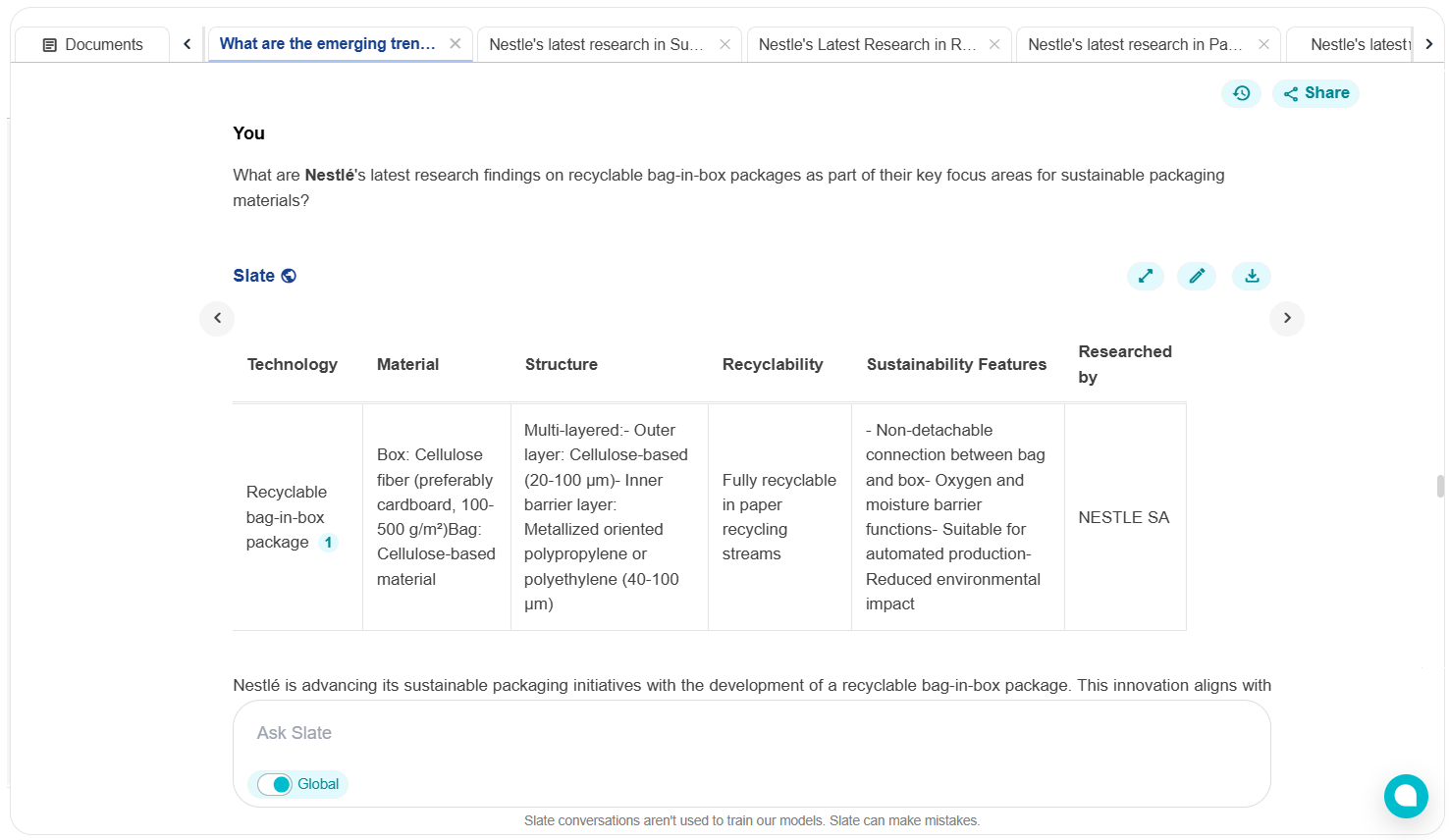
To gain a comprehensive understanding of Nestlé’s recent innovation advancements in different areas, advanced research tools play a crucial role. One such tool is Slate, leverages artificial intelligence to consolidate fragmented research data from patents, scientific publications, and industry reports.
R&D teams can filter innovations by material types, recyclability features, sustainability metrics, and production feasibility. This capability is essential for monitoring how Nestlé’s advancements stack up against those of its competitors and for informing strategic decisions in packaging development.
Let’s explore the key themes and features identified from the research:
1. Cellulose Fiber Materials
Box Construction:
The package features a box made entirely from cellulose fiber materials, such as cardboard, with a grammage ranging from 100-500 g/m². This choice of material ensures that the box is suitable for paper recycling, contributing to the overall sustainability of the package.
Bag Composition:
The bag within the box is also constructed from cellulose-based materials, providing essential oxygen and moisture barrier functions. This design choice enhances the recyclability of the entire package by ensuring that both the box and the bag can be processed together in paper recycling streams.
This move is in line with findings from a 2022 study published in Resources, Conservation, and Recycling, which emphasized that mono-material solutions (especially those based on renewable fibers) achieve up to 75% higher recycling rates than mixed-material packaging in European waste streams (Elsevier, 2022).
2. Multi-layered Structure
Outer Layer (20–100 µm):
The bag’s outermost layer uses a cellulose-based film crucial for structural integrity during handling and transportation. At a thickness of 20 to 100 microns, it achieves a delicate balance that is thin enough for recyclability yet robust enough for durability.
Inner Barrier Layer (40–100 µm):
The inner layer incorporates metallized oriented polypropylene (OPP) or polyethylene (PE), providing necessary barrier properties to protect the product from oxidation and moisture. Nestlé has retained this polymer layer not to compromise product preservation but has engineered it thinly enough (within 40–100 µm) to maintain overall recyclability, as supported by their testing across European lab-certified recycling environments.
3. Non-detachable Connection
Adhesive Technology:
One of the critical process innovations is the non-detachable connection between the bag and box using pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSA). Unlike traditional glued or mechanically separated systems, this design allows automated production line integration to operational efficiency while ensuring the entire package remains a single recyclable entity.
This connection design addresses one of the key pain points in the circular economy: consumer sorting behavior. By preventing disassembly, Nestlé’s packaging eliminates the dependence on end-user recycling compliance and ensures that both components—bag and box—can be processed together.
Research has shown that designs enabling unified recycling streams can increase effective material recovery by up to 35% (Ellen MacArthur, 2021). Nestlé’s application of this insight reflects a deeper operational understanding of material science and consumer and supply-chain behavior.
Uncover Nestlé’s Research in Sustainable Packaging
Nestlé’s advancements in recyclable bag-in-box packaging demonstrate how material innovation, process efficiency, and regulatory readiness hint at what could become the industry standard within a few years.
For R&D teams looking to keep pace with Nestlé’s rapid innovation, leveraging comprehensive competitive intelligence is essential. With Slate, you can uncover performance gaps, track emerging materials and adhesive technologies, and identify whitespace opportunities before they reach the market.
Stay ahead of packaging innovation trends and track exactly what Nestlé and other leaders are researching and patenting in real time. Monitor breakthroughs before they hit the market.
Try Slate and discover how your team can turn research into measurable competitive advantage.


