Across its global portfolio, Nestlé is executing a cohesive sustainability strategy by leveraging its extensive global R&D network to develop next-gen paper-based multilayer packaging. Nestlé has transitioned its iconic products like Smarties and KitKat to fully recyclable paper-based alternatives in Europe.
Recent product launches, such as Vital Proteins paperboard canisters in the U.S. (cutting plastic use by 90%) and Nescafé’s high-barrier paper refill packs in the U.K. (reducing packaging weight by 97%), demonstrate Nestlé’s commitment to reducing environmental impact without compromising product integrity.
This shift is not just a trend but a strategic move that could redefine industry standards. As multilayer paper-based laminates account for 17% of global flexible film production, Nestlé’s advancements in material science and packaging design set a fast-moving benchmark in categories like coffee, dairy, and confectionery.
This research article provides a technical deep dive into Nestlé’s breakthroughs in paper-based multilayer packaging, offering insights for R&D leaders looking to stay ahead of the curve.
Nestlé’s Latest Research in Paper-Based Multilayer Packaging
Nestle’s strategy on paper-based multilayer packaging focuses on enhancing sustainability through innovative designs and materials. The research highlights several key themes and strategies to improve packaging solutions’ environmental impact and functionality.
Nestlé’s innovations are categorized into targeted themes such as oxygen and moisture barrier properties, biodegradability, recyclability, and the incorporation of cellulose-based materials.
As part of this R&D effort, Nestlé is developing high-performance, recyclable paper packaging to replace conventional plastics, especially for oxygen- and moisture-sensitive products like coffee and dairy powders.
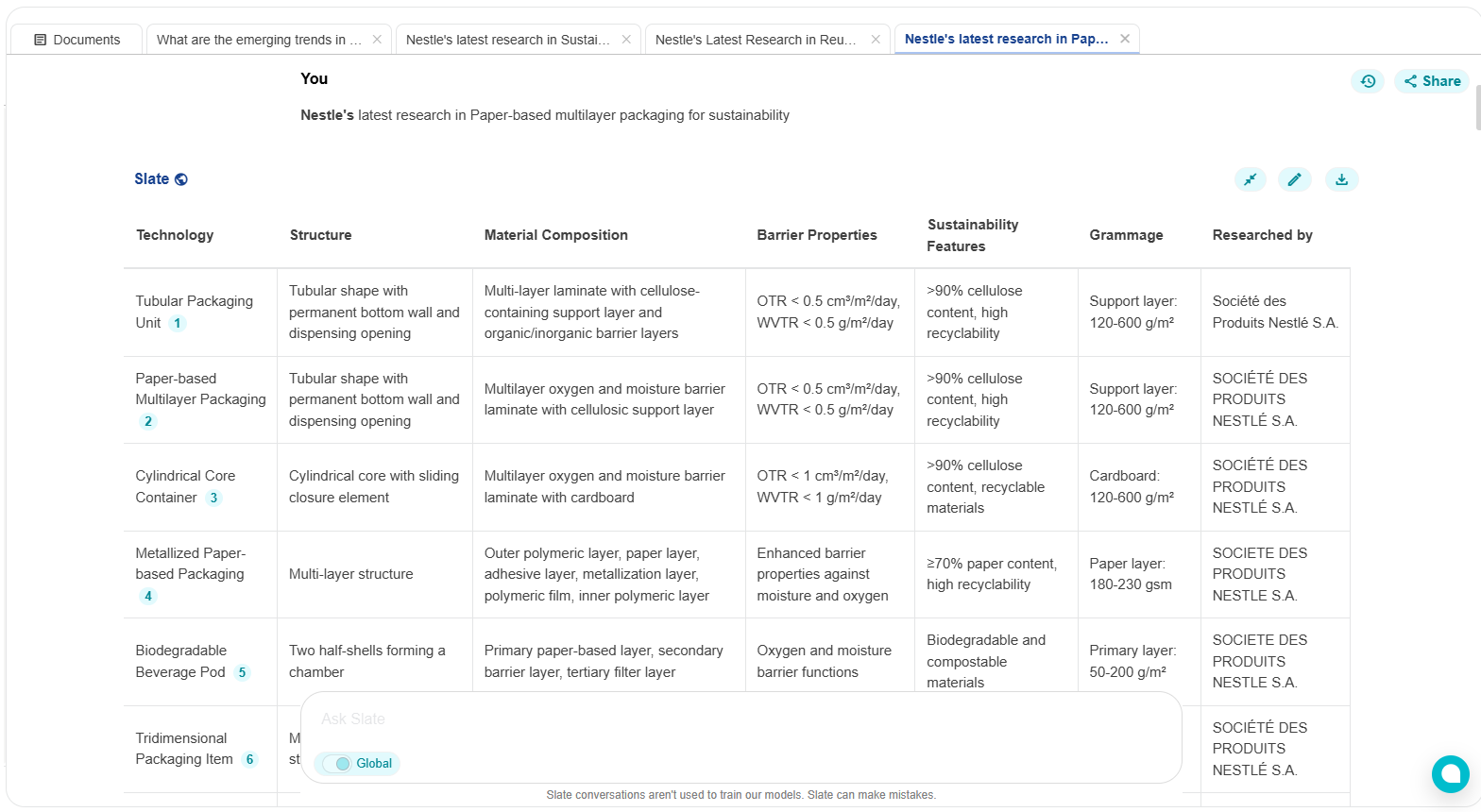
Tools like Slate, helps you find competitors’ advancements in their focus research area. It helps R&D teams or strategic decision-makers benchmark Nestlé’s progress against internal innovation pipelines, uncover potential gaps, and identify collaborative or competitive risks.
By mapping out elements like tubular packaging unit, cylindrical core container, and metallized paper-based packaging, Slate effectively transforms passive research tracking into actionable competitive intelligence.
Let’s explore the key themes and features identified from the research:
1. High Cellulose Content and Barrier Properties
Cellulose-Based Laminates: The packaging units are constructed from multi-layer laminates with a cellulose content exceeding 90%, often over 99%. These laminates provide excellent barrier properties against oxygen and moisture, with an Oxygen Transmission Rate (OTR) and Water Vapour Transmission Rate (WVTR) below 0.5 cm³/m²/day and 0.5 g/m²/day, respectively. This ensures product freshness and extends shelf life while maintaining high recyclability.
Mechanical Stability and Recyclability: The design enhances mechanical stability and handling, aligning with sustainability goals using recyclable materials. This approach is particularly beneficial for food products, offering superior protection compared to traditional paper packaging.
For Nestlé, achieving these low transmission rates with biodegradable, paper-based materials marks a significant leap. It sets a new technical benchmark for shelf-life performance that many paper-based alternatives still struggle to meet, especially in categories like coffee, dairy powders, or confectionery, where oxygen sensitivity is critical.
2. Innovative Structural Designs
Nestlé is also leveraging structural engineering to enhance packaging utility and sustainability:
Tubular and Cylindrical Shapes: The packaging features tubular and cylindrical designs with permanent bottom walls and dispensing openings. These shapes, combined with sliding or removable closure elements, improve functionality and barrier properties, promoting an “open shelf life” that preserves product integrity.
Sliding Closure Elements: The sliding closure elements overlap the core container, enhancing structural stability and barrier properties. This design allows for effective reclosure after initial opening, making it suitable for bulk solids like coffee or milk powder.
These structures are functional and psychologically reinforce premium branding and consumer trust. These elements are critical to gaining share in mature FMCG markets. Rigid paper-based formats are likely to become standard in high-frequency, bulk-product categories.
3. Advanced Material Compositions
Metallized Paper-Based Structures: A multi-layer metallized paper-based material includes an outer polymeric layer, a paper layer, an adhesive layer, a metallization layer, a polymeric film, and an inner polymeric layer. This structure enhances barrier properties while maintaining high recyclability, making it suitable for both dry and liquid food products.
Biodegradable and Compostable Options: Some packaging solutions incorporate biodegradable and compostable materials like Polylactic acid (PLA) and Polybutylene succinate (PBS), allowing for home composting and addressing environmental challenges posed by traditional non-biodegradable materials.
Nestlé uses Polylactic Acid (PLA) and Polybutylene Succinate (PBS), which are home compostable and meet EN 13432 standards. These material combinations indicate a future where high-barrier, fully compostable packaging is commercially viable, setting a roadmap for brands looking to eliminate plastic without compromising shelf life.
Compostable structures that do not compromise on barrier or mechanical performance open new regulatory and retail channels, particularly in Europe and APAC, where Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) frameworks are intensifying. Brands without credible home-compostable solutions may risk exclusion from future sustainable procurement lists.
4. Innovative One-Step Manufacturing Using Cellulosic Pulp
Nestlé’s packaging advancements extend into production with the development of a one-step tridimensional packaging formation process. Key highlights include:
Cellulosic Pulp Molding: The new technique shapes fiber-based packaging into complex 3D forms in a single step, reducing delamination risks.
Enhanced Strength & Barriers: Resulting items offer robust mechanical strength while maintaining low OTR/WVTR values.
This innovation may enable rapid scalability for edible or single-use products (e.g., dairy, confectionery) and could significantly lower production costs compared to multi-step lamination processes. This can potentially open up white-label production avenues for third-party FMCG companies.
Explore Latest Developments in Sustainable Packaging
Nestlé’s advancements in paper-based multilayer packaging signals a decisive shift toward high-performance sustainability. Their innovations in barrier materials, structural design, and manufacturing processes set new benchmarks that are reshaping consumer expectations and regulatory standards across key FMCG categories.
The performance metrics Nestlé achieved especially in barrier properties and recyclability, set a high bar that few in the industry currently meet. Companies that fail to keep up with these developments risk falling behind in both innovation and sustainability commitment.
To navigate this rapidly evolving packaging ecosystem, continuous and detailed monitoring of competitors R&D progress, material innovations, and packaging breakthroughs is essential. This is where Slate, our external innovation discovery platform, becomes a valuable asset.
Slate provides real-time insights into competitor innovations and enable your R&D and strategy teams to identify innovation gaps, benchmark performance, and anticipate market shifts well before they become mainstream.
With Slate – an external innovation discovery platform
- Access consolidate Nestlé’s latest packaging R&D and innovations from diverse sources (patents, research reports, and scientific literature) into one actionable view
- Explore new packaging solutions with detailed performance and environmental impact data
- Monitor competitors’ latest material innovations, packaging strategies, and technology trends to inform your R&D roadmap
- Get data-backed answers to your packaging innovation questions via Slate’s AI research assistant


